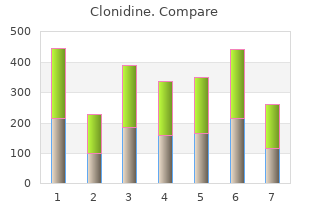
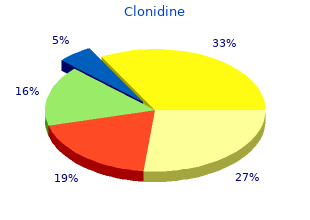
Clonidine
"Safe 0.1mg clonidine, pulse pressure 71".
By: G. Ilja, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Montana College of Osteopathic Medicine
Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy in the administration of continual delicate-tissue conditions blood pressure upon waking up safe 0.1 mg clonidine. Shockwave overview: history and principles International Society for Medical Shockwave Treatment blood pressure chart download excel order 0.1 mg clonidine. Shockwave overview: principles fundamental physics and definition of physical parameters: International Society for Medical Shockwave Treatment blood pressure of 150 100 cheap 0.1 mg clonidine. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy versus placebo for the remedy of continual proximal plantar fasciitis: results of a randomized blood pressure chart bottom number cheap clonidine 0.1mg, placebo-managed, double blinded, multicenter intervention trial. Low-vitality extracorporeal shock wave therapy for painful heel: a potential managed single-blind examine. The use of a cellular lithotripter in the remedy of tennis elbow and plantar fasciitis. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for plantar fasciitis: randomised managed multicentre trial. Ultrasound-guided extracorporeal shock wave therapy for plantar fasciitis: a randomized managed trial. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for continual painful heel syndrome: a potential, double blind, randomized trial assessing the efficacy of a brand new electromagnetic shock wave system. Evaluation of low-vitality extracorporeal shock-wave utility for remedy of continual plantar fasciitis. Intralesional corticosteroid injection versus extracorporeal shock wave therapy for plantar fasciopathy. Comparison of radial shockwaves and standard physiotherapy for treating plantar fasciitis. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy is safe and efficient in the remedy of continual recalcitrant plantar fasciitis: results of a confirmatory randomized placebo-managed multicenter examine. Comparison of two extracorporeal shock wave therapy strategies for the remedy of painful subcalcaneal spur. Location modalities for targeted extracorporeal shock wave utility in the remedy of continual plantar fasciitis. The safety and efficacy of high vitality extracorporeal shock wave therapy in active, moderately active, and sedentary patients with continual plantar fasciitis. Ultrasonographic evaluation of plantar fasciitis after low-stage laser therapy: results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo-managed trial. A randomized managed evaluation of low depth laser therapy: plantar fasciitis. Manipulative therapy for decrease extremity conditions: growth of literature review. Manual physical therapy and exercise versus electrophysical brokers and exercise in the administration of plantar heel pain: a multicenter randomized clinical trial. Conservative chiropractic administration of recalcitrant foot pain after fasciotomy: a retrospective case review. A randomized, managed trial (with blinded observer) of chiropractic manipulation and Achilles stretching vs. Radiation therapy for painful heel spurs: results of a potential randomized examine. Randomized multicenter trial on the impact of radiotherapy for plantar Fasciitis (painful heel spur) using very low doses-a examine protocol. Treatment of plantar fasciitis using 4 completely different local injection modalities: a randomized potential clinical trial. Intralesional autologous blood injection in comparison with corticosteroid injection for remedy of continual plantar fasciitis. Comparison of injection modalities in the remedy of plantar heel pain: a randomized managed trial. Treatment of pain attributed to plantar fasciitis with botulinum toxin a: a brief-time period, randomized, placebo-managed, double-blind examine. Treatment of continual plantar fasciitis with Botulinum toxin A: preliminary clinical results. Efficacy and safety of a single botulinum kind A toxin complex remedy (Dysport) for the relief of upper back myofascial pain syndrome: results from a randomized double-blind placebo-managed multicentre examine. Evidence against set off level injection technique for the remedy of cervicothoracic myofascial pain with botulinum toxin kind A. Botulinum toxin kind B: a double-blind, placebo managed, safety and efficacy examine in cervical dystonia. Does botulinum toxin a combined with bracing forestall hip displacement in children with cerebral palsy and "hips in danger" Computerized gait analysis of botulinum toxin remedy in children with cerebral palsy. Comparison of botulinum toxin injection and neurotomy in patients with distal decrease limb spasticity. A randomised, double blind, placebo managed trial of botulinum toxin in the remedy of spastic foot in hemiparetic patients. A single-blinded, randomized pilot examine of botulinum toxin kind A combined with non-pharmacological remedy for spastic foot. Ultrasonographic guided botulinum toxin kind A remedy for plantar fasciitis: an consequence-based mostly investigation for treating pain and gait adjustments. Comparison of ultrasound-, palpation-, and scintigraphy-guided steroid injections in the remedy of plantar fasciitis. Examining the degree of pain discount using a multielement exercise model with a conventional coaching shoe versus an ultraflexible coaching shoe for treating plantar fasciitis. Intracorporeal pneumatic shock utility for the remedy of continual plantar fasciitis: a randomized, double blind potential clinical trial. Percutaneous fenestration of the anteromedial aspect of the calcaneus for resistant heel pain syndrome. A new minimally invasive technique for treating plantar fasciosis using bipolar radiofrequency: a potential analysis. Operative consequence of partial plantar fasciectomy and neurolysis to the nerve of the abductor digiti minimi muscle for recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. Degenerative lesions of the plantar fascia: surgical remedy by fasciectomy and excision of the heel spur. Lateral column symptomatology following plantar fascial launch: a potential examine. Nonunion of a fracture of the sustentaculum tali inflicting a tarsal tunnel syndrome: a case report. Acute tarsal tunnel syndrome following partial avulsion of the flexor hallucis longus muscle: a case report. Benign joint hypermobility with neuropathy: documentation and mechanism of tarsal tunnel syndrome. Tarsal tunnel syndrome: evaluation of remedy consequence with an anatomic pain depth scale. Usefullness of electrodiagnostic strategies in the evaluation of suspected tarsal tunnel syndrome: an evidence-based mostly review. Sonography as an aid to neurophysiological studies in diagnosing tarsal tunnel syndrome. Musculoskeletal problems of the decrease limb-ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging correlation. Morphological and functional adjustments in the diabetic peripheral nerve: using diagnostic ultrasound and neurosensory testing to choose candidates for nerve decompression. Use of ultrasonographic steering in interventional musculoskeletal procedures: a review from a single institution. Two weeks of prednisolone was as efficient as 4 weeks in bettering carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms J Bone Joint Surg Am. A randomised clinical trial of oral steroids in the remedy of carpal tunnel syndrome: a long run follow up. Efficacy of splinting and oral steroids in the remedy of carpal tunnel syndrome: a potential randomized clinical and electrophysiological examine. Wrist injuries in adolescent gymnasts of a Chinese opera school: radiographic survey. A comparison of the lidocaine patch 5% vs naproxen 500 mg twice day by day for the relief of pain associated with carpal tunnel syndrome: a 6-week, randomized, parallel-group examine. Lidocaine patch 5 for carpal tunnel syndrome: how it compares with injections: a pilot examine. Topical lidocaine patch relieves postherpetic neuralgia more effectively than a automobile topical patch: results of an enriched enrollment examine.
Thus hypertension young trusted clonidine 0.1 mg, we might establish two popu U hthoff63 noticed m esenchym al cells and a plethora lations of fibroblasts: those with intracellular contractile of tenoblasts blood pressure medication lotrel safe clonidine 0.1 mg, and Regan et al blood pressure heart attack generic 0.1mg clonidine. Those authors term ed the condition angiofibro to blood pressure for children safe 0.1mg clonidine the course of collagen fibers, although m any fibro blastic tendinosis as a result of angiofibroblastic tissue was blasts had been discovered close to cleavage planes within the tendons discovered to be insinuating itself by way of abnorm al hyper in addition to in perivascular areas. Sarkar and U hthoff63 cellular regions and lengthening focally into adjacent identified m yofibroblasts close to vascular regions, and we norm al-appearing tendon fibers. A cute inflam m atory noticed these cells close to and at a distance from blood cells alm ost always had been absent, however persistent inflam m a vessels. M any dinosis was famous by G oldie20 and was later described vessels had a constricted or obliterated lum en27,62,sixty seven. The collagen m atrix within the regions surrounding of authors have described a proliferative arteriolitis the vascular hyperplasia was of poor quality, and the with som e deposition of fibrin and the shape ation of vessels com m only had been seen within the m ost abnorm al a throm bus, with obliteration of the lum en of the ves appearing areas of collagen. It is cheap to think about the vascular and fibro In the current examine, gentle m icroscopy of sections blastic hyperplasia in tendinosis as a physiological re that had been stained with hem atoxylin and eosin con sponse to disruption of the collagen structure. The sistently revealed vascular hyperplasia within regions of structure and physiology of norm al tendon collagen has tendinosis (Figs. Vessel-like constructions had been been properly described in a number of recent studies17-19,26,69,72. This linear structure other areas, sm all-lum en vessels had been surrounded by takes on the secondary quality of a left-handed config swirls of abnorm al collagen and dense populations of uration. Light m icroscopy of sections that had been which might be coiled to kind a proper-handed helix. This prod stained with M asson trichrom e and vim entin stain re uct, secreted by G olgi vesicles and trim m ed enzym ati vealed that the vascular hyperplasia was m uch m ore cally of its carboxyl and am ino term inals extracellularly, widespread and disorganized than it appeared on sec strains up alongside other procollagen m olecules in a tions that had been stained with hem atoxylin and eosin quarter-stagger arrangem ent (creating a quarternary (Figs. There was no apparent course to the structure), as determ ined by common affiliation with vascularity, nor was there any proof of a connection adjacent m olecular acidic and primary am ino acids. Five collagen m olecules m ake up a single m icrofibril Im m unohistochem ical research that had been perform ed of tendon19,35,forty,sixty six,72. These m ature vascular elem ents regardless of whether the ves collagen subunits are internally bound by a m atrix of sels within the area of tendinosis had been the result of extrinsic proteoglycans and glycosam inoglycans. They are m ain capillary ingrowth or the product of an intrinsic m esen tained by a sparse inhabitants of tendon fibroblasts that chym al response. The ultim ate dinosis are able to sustaining blood circulate or if such structure of tendon is a three-dim ensional one. When a blood circulate can be sufficient to maintain the rem odeling tear occurs within a tendon fascicle, it disrupts a nor strategy of tendon-healing. O nly the partitions of the larger m ally balanced system in a m anner som ewhat analo vessels stained positively for elastin. Sim ilar to a stress elastin develops within the partitions of m ore m ature vessels and fracture, which heals both by the physiology of native that the im m ature vessels seen in regions of tendino osteons or by way of a kind al system of callus kind ation, sis characterize a structurally incom plete process (Fig. The collagen in tendinosis is abnorm al each grossly In the current examine, the vascularity of tendinosis and on examination ination with gentle and electron m icroscopy. Blood vessels had reduplicated and thickened elbow is determined by the visible identification of tissue that basal lam ina. A t tim es, the lining cells (pericytes) ap is boring, grey, and soft com pared with shiny, white, agency, peared a number of layers thick and contained contractile norm al-appearing tendon42. The m atrix, which is com posed prim arily of proteoglycans, glycosam inoglycans, and water, is stained evenly. No vascular constructions are apparent inside the tendon (hem atoxylin and eosin, one hundred). The whole specim en seems to be hypercellular, with focal areas which might be densely cellular. The area in which angiofibroblastic hyperplasia (proper asterisk) m eets norm al tendon (left asterisk) incorporates active fibroblasts which might be random ly oriented and seem to be infiltrating the encircling tissue. The m atrix inside the pathological areas is loose and pale in appearance (hem atoxylin and eosin, one hundred). The infiltrative appearance (double solid arrow) of tendinosis and the distinct boundary of norm al tendon suggest a reparative and regenerative process ( forty). D ensely cellular regions (indicated by the purple stain) reveal angiofibroblastic hyperplasia perm eating the tendon in linear clefts and clusters. The appearance of this specim en should be contrasted with that of the specim en in Fig. In the incom plete restore process but also a physiological loss present examine, we famous sim ilar findings but also discovered of com m unication between the native healing process that m ultiple ranges of m agnification and marking tech and the norm al tendency of the body to restore the niques revealed not only structural disruption and an unique structure. This discovering is indicated by the presence of widespread cellularity and random ly oriented vascular hyperplasia (vim entin, forty). It has been instructed that, within the dam aged tendon, the tenocyte dedifferentiates into a m esenchym al cell, which is capable of becoming vascular, adipose, chondroid, osseous, or fibroblast cell varieties. Low-energy m agnification of sections that had been had been som etim es dem arcated by fibroblastic hyperplasia, stained with hem atoxylin and eosin revealed the shape a as if these cells had m ultiplied in response to the native tion of longitudinal clefts between fascicles; the clefts stress of the shearing tears. The stellate cytoplasm ic shape with projections into the encircling m atrix is quiescent, missing proof of an active production response. The nucleus-to-cytoplasm ratio is excessive, the nucleus is centralized, and the chrom atin is condensed at the center of the nucleus (solid arrow). The collagen m atrix has organized bundles of uniform ly sized collagen fibrils and lacks debris within the ground substance ( 5130). The cytoplasm is loaded with m itochondria, endoplasm ic reticulum, and vacuoles, presum ably for secretion. Pale-grey condensations alongside the cytoplasm ic border are contractile elem ents (arrows), which m ay allow cellular m ovem ent. The surrounding collagen m atrix is disorganized and unrem odeled, and debris is apparent within the ground substance ( 4275). M asson-trichrom e staining of distinction between the planes of tendon fascicles of a m ore severely affected specim en revealed the for (Fig. It is believed that the tenocytes in injured tendons dedifferentiate into pluripotent m esenchym al cells, leading to native m etaplasia (sm ooth m uscle antigen, 50). D espite the presence of a vessel lum en (asterisk), a dense assortment of fibroblasts is seen to contain areas of hypoxic granulation (arrow). The collagen m atrix and the ground substance are in disarray and are stuffed with debris. The fibroblasts to which the norm al colla whereas staining for elastin confirmed nests of tendinosis gen appeared to be hooked up had a excessive nucleus-to insinuated between fibers of norm al collagen (Fig. In cytoplasm ratio and contained condensed chrom atin addition, the collagen in areas of tendinosis was each within a nucleus containing one centriole. The cyto built-in into the encircling m atrix and appeared as plasm was sparsely vacuolated. Each cell was stellate a separate m ass of unrem odeled collagen and m atrix with projections into the encircling collagen m atrix production. The findings of electron m icroscopy provide an ex In the current examine, electron m icroscopy revealed planation for the abnorm al appearance of collagen in that the abnorm al collagen within the regions of tendinosis tendinosis. Norm ally, tendon collagen seems to have was com posed of particular person strands, which had been of nor approxim ately a sixty-4-nanom eter-broad, triple heli m al width and had a norm al periodicity of banding pat cal, quarter-stagger arrangem ent. The background m a described disintegration of collagen fibrils, longitudinal trix was loose and was filled with what appeared to be splitting, abnorm al fibril diam eters, bubble kind ation, debris. O n cross section, collagen fibers from the area angulation, and knick deform ations (folding of the sur of tendinosis had been of variable diam eter, with an uneven face of collagen fibrils, normally within the internal curves of the m ixture of thick and skinny fibrils. W ithin the did such poorly kind ed m aterial provide proof of specim ens, nevertheless, there were norm al-appearing re com bining with or becom ing norm al tendon. From a gions that served as an inside basis for com parison structural perspective, the ultrastructure of collagen in (Figs. The longitudinal sections confirmed uni tendinosis is unable to maintain a tensile load (Fig. These Associated Findings fibrils had been parallel to one another and extended long distances in sheets without gaps. Vessels had been abnorm al and contained reduplicated basal lam ina and pericytes in m ultiple layers, a thickened internal lining, and som e gaps within the basal lam ina ( 8550). O ther m esenchym e-derived cells and bone m orphogenic protein can convert periosteal in tendinosis include osteocytes, chondrocytes, pericytes, m esenchym al stem cells into chondrocytes and osteo and adipocytes27,35,69. The general structural arrangem ent is organized in parallel bundles with no fragm entation and good cross-linkage ( 10,260). In the current examine, examination ination of 1 had been noticed in abnorm al-appearing regions, however true specim en that had been stained with neurofilam ent im adipocytes hardly ever had been seen.
Order 0.1 mg clonidine. How To lower Blood Pressure Naturally With Nattokinase And Exercise.
Consequently prehypertension range buy 0.1mg clonidine, with out detracting from the intent of the above definition blood pressure chart in elderly cheap clonidine 0.1 mg, referred pain could be outlined more strictly in neurological phrases as pain perceived as arising or occurring in a region of the physique innervated by nerves or branches of nerves aside from those who innervate the actual source of pain arteria digitalis palmaris communis proven clonidine 0.1mg. In the context of spinal pain blood pressure names buy clonidine 0.1 mg, referred pain may occur within the head (Campbell and Parsons 1944; Feinstein et al. Referred pain within the decrease limb could also be certified using commonplace anatomical phrases that describe its Scapular Pain: Pain perceived as arising topographic location, viz. This precision glenohumeral joint, centered over the lateral margin of avoids the ambiguity of phrases such as �higher cervical the acromion. Physiology: the anatomical foundation for spinal Posterior Shoulder Pain: Pain focused over the referred pain appears to be convergence. In the absence of any additional in accordance with the topographic segment encompassed localizing info, the mind is unable to decide using commonplace anatomical definitions, viz. Convergence is often segmental in nature, in that must be described in such phrases. This is as a result of pain within the stimulation of beforehand damaged nerve roots, back tends to not discriminate a lot among the different inflammation of a dorsal root ganglion, and possibly by diagnostic groups. Acute back pain is usually cramping or knifelike, but Ectopic activation results in pain being perceived as could also be merely uninteresting or aching. Chronic back pain and not using a radicular Radicular pain differs from referred pain in a number of component is mostly aching, uninteresting, or burning or any respects. It additionally tends to be the disease processes that cause radicular pain are made worse by movement. While additionally perceived deeply, radicular pain nonetheless has a cutaneous high quality in proportion to the number of Campbell, D. It stems from an period when the mechanisms joint pain patterns I: a examine in normal volunteers, Spine, 15 of referred pain and radicular pain have been poorly (1990)453-457. The symptom of spinal pain must be described in For conditions which might be thought-about still controversial phrases of its location and nature using the definitions or unproven, the Committee has formulated criteria that supplied on pages 11 and 12; these descriptions, must be absolutely happy before the analysis is ascribed. The Committee additionally accepts the use of such diagnoses As far as potential, the actual analysis of spinal on a presumptive foundation with out the criteria being pain must be expressed concurrently alongside two axes: happy. However, it posterior thigh and calf due to stenosis of the L4-5 is mentioned within the context of spinal pain for not intervertebral foramen. Foraminal stenosis due to vertical subluxation of the When associated with spinal pain, the spinal pain intervertebral joint, osteophytes stemming from the warrants an impartial classification to which the zygapophysial joint or intervertebral disk, buckling of classification of the radicular pain may then be the ligamentum flavum, or a mixture of any of appended. Prolapsed intervertebral disk material that elicits an independently, supplemented if required by a inflammatory reaction within the vertebral canal that classification of the radiculopathy. Radiculitis brought on by inflammatory exudates leaking extent or distribution of referred pain has no bearing on from an intervertebral disk within the absence of frank the underlying explanation for the spinal pain. Radicular Pain and Radiculopathy Remarks: Radicular pain must be distinguished from referred pain (see above). Radicular pain may occur alone, within the absence of Clinical Features: the pain is lancinating in spinal pain, whereupon it must be categorised as limb high quality and travels alongside a slim band. The former relates to objective Radiculopathy may occur in isolation or in association neurological indicators due to conduction block. X1kC, Where spinal and radicular pain occur, the suffixes S while concomitant radicular pain within the arm could be and R are used, respectively. X4 X-8 Thoracic Spinal Pain of Unknown or Uncertain Origin S/C codes R only/in addition X-8. X7cS X-10 Thoracic Zygapophysial Joint Pain S/C codes R only/in addition X-10(S) Thoracic Zygapophysial Joint Pain Trauma 333. X7dR X-sixteen Radicular Pain Attributable to a Prolapsed Thoracic Disk S/C codes R only/in addition X-sixteen(R) Radicular Pain Attributable to a Prolapsed Thoracic Disk Trauma 303. Local Syndromes of the Upper Limbs and Relatively Generalized Syndromes of the Upper and Lower Limbs 1. Where spinal and radicular pain occur, the suffixes S and R are used, respectively. If a radicular pain happens in an space with a special location it must be coded moreover. X8fS * the asterisk is inserted in spinal and radicular codes where no letter is required within the sixth place. Sacral Spinal or Radicular Pain Syndromes * Note: S codes embrace R codes unless specified as �S only. X0*R * the asterisk is inserted in spinal and radicular codes where no letter is required within the sixth place. X3a Arms: inflammatory or immune reactions Prevalence: frequent in neuropathies of diabetes, amy 203. X8a Arms: unknown or different (for which see I-36), neuralgic amyotrophy, Fabry�s 603. Main Features Social and Physical Disabilities Sharp, usually jabbing pain in stump, usually aggravated Decreased mobility. Believed to be more com mon if lack of limb happens later in life, in limbs than in Associated Symptoms breast amputation, within the breast before the menopause Refusal to utilize prosthesis. Phantom limb pain is almost all the time associated with Usual Course distorted image of misplaced half. Develops a number of weeks to months after amputation; persists indefinitely if untreated. Associated Symptoms Aggravated by stress, systemic disease, poor stump Relief health. Social and Physical Disabilities Essential Features May preclude gainful employment or normal daily ac Pain in stump. Related to deafferentation of neurons and their sponta neous and evoked hyperexcitability. The pain is incessantly described as burning and steady and exacerbated by movement, In the previous edition of this classification, causalgia steady stimulation, or stress. Guarding of the af servation that in certain circumstances sympatholytic interven fected half is usually noticed. The drome, Type I (Reflex Sympathetic bone uptake part of a 3-part bone scan may re Dystrophy) (1-4) veal a attribute pattern of subcutaneous blood pool adjustments. It is associated at Relief some point with evidence of edema, adjustments in pores and skin In circumstances with sympathetically maintained pain, sym blood move, irregular sudomotor exercise within the region of patholytic interventions may provide momentary or the pain, or allodynia or hyperalgesia. Site Complications Usually the distal side of an affected extremity or with Phlebitis, inappropriate drug use, and suicide. The presence of an initiating noxious event, or a Associated Symptoms and Signs explanation for immobilization. Continuing pain, allodynia, or hyperalgesia with tions in hair progress, and lack of joint mobility may oc which the pain is disproportionate to any inciting cur. Sympathetically blood move, or irregular sudomotor exercise within the maintained pain could also be current. Definition Complications Burning pain, allodynia, and hyperpathia usually within the Phlebitis, inappropriate drug use, and suicide. Social and Physical Impairment Inability to perform activities of daily residing and occupa Site tional and recreational activities. Main Features Diagnostic Criteria the onset usually happens instantly after partial nerve 1. Spontaneous pain happens which is described as con blood move, or irregular sudomotor exercise within the stant and burning, and is exacerbated by mild contact, region of the pain. It may embrace all or most of one facet, Social and Physical Disabilities all components of the physique caudal to a stage (just like the decrease half this pain is a good bodily and psychological burden to of the physique), or each extremities on one facet. In consequence their social life and work be restricted simply to the face or part of one extremity. The onset may Cerebrovascular lesions (infarcts, hemorrhages), multi be instantaneous but usually happens after a delay of ple sclerosis, and spinal wire accidents are probably the most com weeks or months, hardly ever a few years, and the pain in mon causes. Pain Quality: many different qualities syringomyelia, syringobulbia, and spinal vascular mal of pain occur, the most typical being burning, aching, formation, and may occur after operations like cor pricking, and lancinating. There could also be various neurological signs and indicators such as monoparesis, hemiparesis, or paraparesis, to Differential Diagnosis gether with somatosensory abnormalities within the affected Nociceptive, peripheral neurogenic, and psychiatric areas.
Neprilysin-poor knockout mice show each Alzheimer�s-like behavioral impairment and amyloid-beta deposition within the brain define pulse pressure quizlet safe clonidine 0.1mg,165 providing strong evidence for the protein�s affiliation with the Alzheimer�s illness process blood pressure z score calculator safe clonidine 0.1 mg. Indeed prehypertension prevalence generic 0.1mg clonidine, some consider that neprilysin is the speed limiting molecule in amyloid beta degradation hypertension headaches quality clonidine 0.1 mg. Higher levels of inappropriately oxidized neprilysin have been present in Alzheimer�s patients compared to cognitively regular aged individuals. Self-propagative replication of A oligomers suggests potential transmissibility in Alzheimer illness. Lack of neprilysin suffices to generate murine amyloid-like deposits within the brain and behavioral deficit in vivo. Etiology of sporadic Alzheimer�s illness: somatostatin, neprilysin, and amyloid beta peptide. The lead researcher explains what they found: Tau may be compared to railroad ties that stabilize a prepare observe that brain cells use to transport meals, messages and other vital cargo all through neurons. In Alzheimer�s, modifications within the tau protein trigger the tracks to become unstable in neurons of the hippocampus, the middle of memory. The abnormal tau builds up in neurons, which finally results in the demise of these neurons. Amyloid, on the other hand, starts accumulating within the outer components of the cortex and then spreads right down to the hippocampus and finally to other areas. Our examine exhibits that the buildup of amyloid has a powerful relationship with a decline in cognition. When you account for the severity of tau pathology, nonetheless, the connection between amyloid and cognition disappears � which indicates tau is the driving force of Alzheimer�s. Every neuron has a cytoskeleton, an inner help structure partly made up of structures known as microtubules. These microtubules act like tracks, guiding vitamins and molecules from the physique of the cell to the ends of the axon and back. Tau protein is a microtubule-related protein,171 expressed in neurons and glia, that stabilizes microtubules within the cell cytoskeleton � especially in axons, where it seems to play a job in establishing neuronal 169 Giacobini E, Gold G. Clinicopathologic and 11C-Pittsburgh compound B implications of Thal amyloid phase across the Alzheimer�s illness spectrum. Inhibition of neurite polarity by tau antisense oligonucleotides in major cerebellar neurons. Alzheimer�s illness-sort neuronal tau hyperphosphorylation induced by A beta oligomers. Neocortical neurofibrillary tangles correlate with dementia severity in Alzheimer�s illness. In Alzheimer�s illness, aggregating tau proteins trigger microtubules to disintegrate. Peroxynitrite induces Alzheimer-like tau modifications and accumulation in rat brain and its underlying mechanisms. Acetylated tau, a novel pathological signature in Alzheimer�s illness and other tauopathies. Post-translational modifications of tau protein: implications for Alzheimer�s illness. Neuronal loss correlates with but exceeds neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer�s illness. Tau protein abnormalities associated with the progression of Alzheimer illness sort dementia. Specific concentrating on of tau oligomers in Htau mice prevents cognitive impairment and tau toxicity following injection with brain-derived tau oligomeric seeds. Coming to an understanding of how poisonous tau species seed and spread by way of the brain would seem to be a needed precondition for finding efficient standard remedies for neurodegenerative tauopathies. Studies in cell culture and genetically modified mouse models counsel that tau might usually facilitate or enhance excitatory neurotransmission by regulating the distribution of synaptic exercise-associated signaling molecules. Tau mislocalization to dendritic spines mediates synaptic dysfunction independently of neurodegeneration. Exosome-related tau is secreted in tauopathy models and is selectively phosphorylated in cerebrospinal fluid in early Alzheimer illness. Diagram displaying two neurons and a capillary blood vessel within the brain, illustrating 199 key cellular and molecular pathologies in Alzheimer�s illness (from Huang and Mucke, 2012). Transforming growth factor beta2 autocrinally mediates neuronal cell demise induced by amyloid-beta. Amyloid beta protein is neurotoxic to mature neurons in culture at greater concentrations; in differentiated neurons, amyloid beta protein causes dendritic and axonal retraction followed by neuronal demise. When expressed within stressed neurons, ApoE4 is cleaved, to a a lot greater extent than ApoE3, into neurotoxic ApoE fragments that disrupt the cytoskeleton and impair mitochondrial functions. Mitochondrial Abeta: a potential explanation for metabolic dysfunction in Alzheimer�s illness. The amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer�s illness: an appraisal for the event of therapeutics. These properties have been compared to these of prions, totally different types of which trigger Jacob-Creutzfeldt illness, scrapie and mad-cow illness (Section 6. These inclusions have related structural features to �classical� Lewy our bodies seen subcortically in Parkinson�s illness. Additionally, a lack of dopamine-producing neurons (within the substantia nigra) happens, much like that seen in Parkinson�s illness, and a lack of acetylcholine-producing neurons (within the basal nucleus of Meynert and elsewhere) much like that seen in Alzheimer�s illness. Autopsy sequence reveal that when Lewy physique inclusions are found within the cortex, they usually co occur with Alzheimer�s illness pathology found primarily within the hippocampus, including senile plaques, and granulovacuolar degeneration (grainy deposits within and a clear zone round hippocampal neurons). Pathogenic protein seeding in Alzheimer illness and other neurodegenerative disorders. Evidence for human transmission of amyloid pathology and cerebral amyloid angiopathy. See additionally commentary: �Alzheimer�s illness could also be transmittable,� Washington Post, 10 Sep 2015;. One examine of the human principal inferior olivary nucleus found oligodendrocytes (-46%) have been lost in related proportions as neurons (-34%), whereas the number of astrocytes decreased only barely. The inflammatory response system of brain: implications for therapy of Alzheimer and other neurodegenerative ailments. Neuroglia within the inferior olivary nucleus during regular growing older and Alzheimer�s illness. Cell number modifications in Alzheimer�s illness relate to dementia, to not plaques and tangles. When such is detected, microglia set off the discharge of substances that recruit other microglia to the scene which then destroy and do away with any international invaders. Microglia additionally work as garbage collectors and stop inflammation by chewing up lifeless cells, misfolded proteins, and other molecular particles strewn amongst dwelling cells including A clusters that mixture as gummy deposits and break the connections between neurons, causing lack of memory and spatial consciousness. In the brainstem, lack of median raphe and locus coeruleus neurons results in deficits in serotonin and norepinephrine, respectively. Prostaglandin signaling suppresses helpful microglial function in Alzheimer�s illness models. Amyloid triggers in depth cerebral angiogenesis causing blood brain barrier permeability and hypervascularity in Alzheimer�s illness. Amyloid contributes to blood-brain barrier leakage in transgenic human amyloid precursor protein mice and in humans with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neuroinflammation � an early occasion in each the historical past and pathogenesis of Alzheimer�s illness. Activation of the unfolded protein response is an early occasion in Alzheimer�s and Parkinson�s illness. Herpes simplex virus infection causes cellular beta amyloid accumulation and secretase upregulation. Occupational risk factors in Alzheimer�s illness: a review assessing the quality of published epidemiological research. A review of epidemiologic research on aluminum and silica in relation to Alzheimer�s illness and related disorders.